What Is a Microgrid?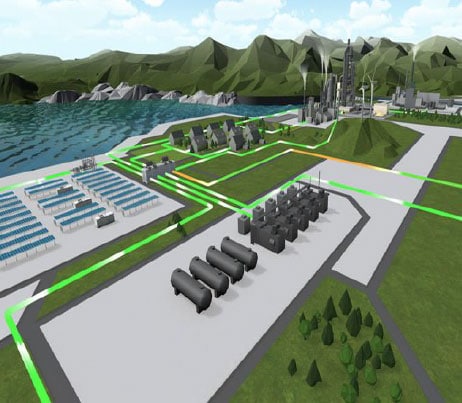
A microgrid is a discrete energy system consisting of distributed energy sources (including demand management, storage, and generation) and loads capable of operating in parallel with, or independently from, the main power grid. The primary purpose is to ensure local, reliable, and affordable energy security for urban and rural communities, while also providing solutions for commercial, industrial, and federal government consumers. Benefits of microgrids that extend to utilities and the community at large include lowering greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and lowering stress on the transmission and distribution system and reducing energy costs.
Microgrids modern, small-scale versions of the centralized electricity system. Microgrid infrastructures achieve specific local goals, such as reliability, carbon emission reduction, diversification of energy sources, and cost reduction, established by the community being served.
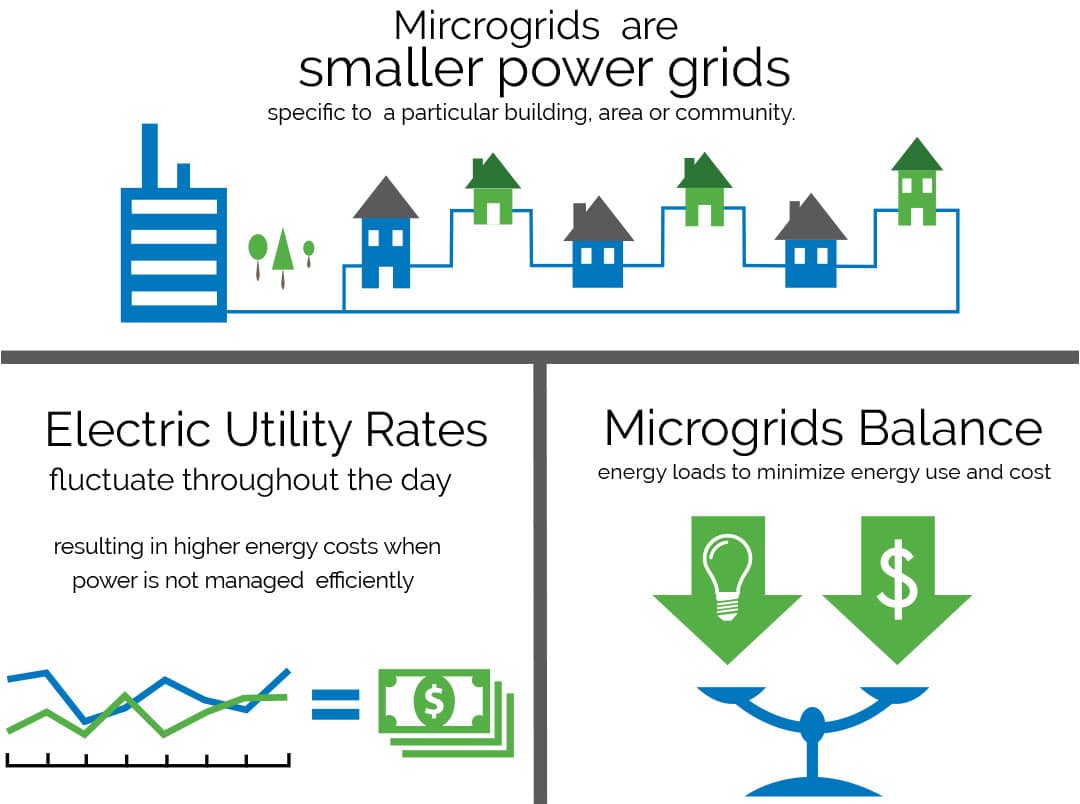
Microgrids in power systems focus on resilient power supplies at a wide range of types of businesses, communities and other environments as well as to allow the increased penetration of renewables. This has spurred the creation of new technologies and control mechanisms that allow microgrids to operate in a grid-connected model and also independently for extended periods of time.
These activities are leading to the development of a new concept referred to as the “dynamic microgrid” – a top-down breakup of the distribution grid into an interconnected set of microgrids. Such a microgrid infrastructure would radically change utilities’ business models and how they address storm response as well as deliver their many other mandates.
We also offer a “Bridge to Grid Power” solution designed to provide reliable and efficient energy during transitional periods. This solution is ideal for industries and communities needing temporary power while permanent infrastructure is being developed or upgraded. By leveraging advanced technologies and a wide range of power generation products, we ensure seamless energy supply.
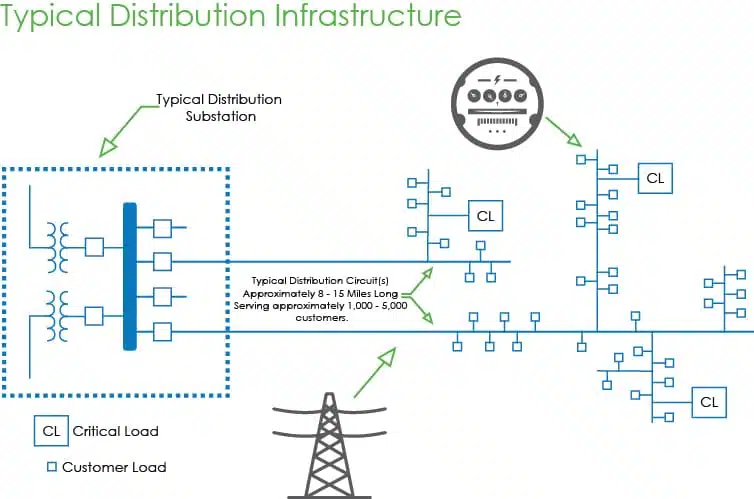
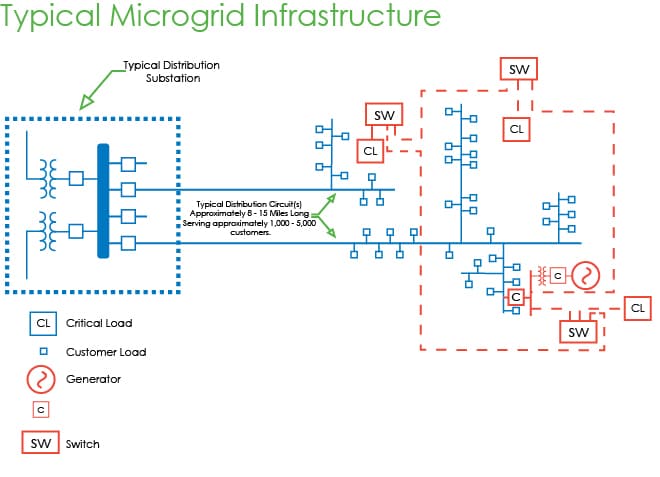
Benefits of Microgrid – Value Proposition
Efficiency
- Reduce fuel consumption
- Supply close to demand to minimize distribution losses
- Combined electricity and heat generation
Reliability
- Optimally manage on-site energy resources 24/7
- Power quality and reliability at the local level
Energy Security
- Ensure energy supply for critical loads utilizing on-site generation
- Grid independence capability
Economic Savings
- Peak Shaving/Load shifting and supply management with demand response
- Enables hedging against energy cost fluctuation
- Reduction of cost of electricity with on-site generation and effective energy management
Sustainability
- Reduction of carbon footprint by integrating cleaner fuel resources
Reach out to Martin Energy Group the next time you find yourself asking, “What is a microgrid?”
Case Study: Fisher Ranch Produce Blythe, CA
- 3.5 MW Natural Gas Generators
- 637 KW Solar Photo Voltaic array
- 4 MW Utility Scale Battery Storage
- Online Power Conversion System (PCS)
- 160 Tons Ammonia Absorption Chiller
- Smart Controls with remote operation and self healing
- Island Power System –No Grid Connection
